Forehead acne causes and treatments

Wondering how you can get rid of unwanted blemishes on your forehead? If so, you're not alone in your mission to achieve clear, glowing skin. For both men and women, the T-zone (nose, chin, and forehead) is notorious for being an area prone to breakouts due to its increased sebum production and large hair follicles.
What causes forehead pimples?
The frustrating answer is a lot of things. Blemishes can appear on the forehead due to several different reasons. Like most acne types, excess oil production, dead skin cells, dirt, bacteria such as P. acnes, and fungi contribute to the formation of forehead pimples by clogging up the pores of sebaceous glands.
Though it can be a bit intimidating, one of the first steps to treating acne pimples is to figure out why they're developing in the first place. Here are some things that may be contributing to your breakouts.
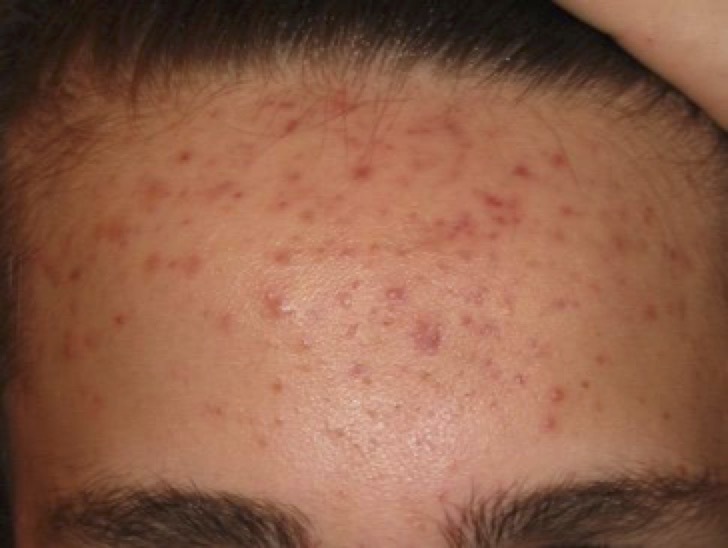
Why Do Forehead Pimples Happen?
Forehead acne doesn’t have one single culprit—it’s a mix of factors that clog pores and trigger breakouts. The main culprits? Excess oil, dead skin cells, dirt, bacteria (P. acnes), and even fungi. Here’s a closer look at some common triggers:
1. Your Hair
Oily hair and scalp can transfer oils to your forehead, leading to clogged pores. Hair products like gels and sprays often contain acne-triggering ingredients like cocoa butter or coconut oil. Bangs? They can trap dirt and oil against your skin, creating the perfect environment for breakouts.
Pro Tip:
- Wash your hair regularly, especially if it’s oily.
- Choose non-comedogenic hair products.
- Keep bangs off your forehead to prevent pore blockages.
2. Pore-Blocking Cosmetics
Some makeup and skincare products can clog pores, especially if they contain oils, lanolin, or synthetic fragrances. Look for products labeled non-comedogenic to avoid worsening breakouts.
3. Stress
Stress doesn’t directly cause acne, but it does increase cortisol, the “stress hormone.” Cortisol stimulates oil production, disrupts your skin’s barrier, and slows down cell turnover—all of which can trigger acne.
4. Diet
High-glycemic foods (like sugary snacks and white bread) can lead to inflammation, which may worsen acne. Swap these for anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, fish, and nuts.
What Type of Forehead Acne Are You Dealing With?
Not all acne is created equal. Here are the types of forehead acne you might encounter:
1. Bacterial Acne
Often caused by friction from hats, helmets, or headbands, this type of acne results from bacteria clogging pores. Treatment? Benzoyl peroxide (2.5%) works wonders.
2. Fungal Acne
Caused by an overgrowth of yeast (Malassezia folliculitis), fungal acne appears as small red bumps, often in uniform clusters. It’s itchy and thrives in oil-rich areas like the forehead.
Best Treatments:
- Use a salicylic acid cleanser to exfoliate and control oil.
- Try antifungal options like ketoconazole (Nizoral shampoo).
- Avoid heavy, oily skincare products.
3. Subclinical (Comedonal) Acne
These are small, flesh-colored or red bumps under the skin—basically the first stage of a zit. They’re often triggered by poor hygiene, over-washing, or hormone imbalances.
Best Treatments:
- Incorporate a salicylic acid cleanser or toner.
- Use a retinol cream (0.25%–0.5%) to encourage cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
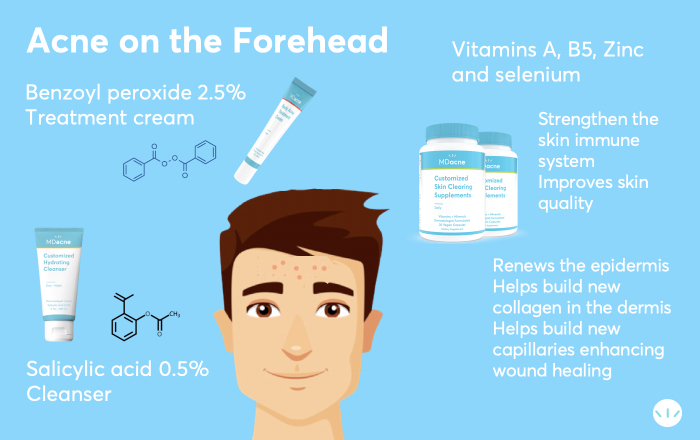
How to Treat Forehead Acne
Ready to fight back? Here’s a list of effective treatments for forehead acne:
1. Benzoyl Peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide is a powerhouse ingredient kills acne-causing bacteria, unclogs pores, and reduces inflammation. Look for over-the-counter products with 5% or less to avoid dryness.
2. Salicylic Acid
A gentle exfoliator that unclogs pores, reduces oil, and clears blemishes. Salicylic acid is perfect for sensitive skin and typically causes less irritation than benzoyl peroxide.
3. Topical Retinoids
Retinol works wonders for both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne. It increases cell turnover, clears clogged pores, and reduces scarring. Start with a lower concentration (0.25%) and work your way up.
How to Prevent Forehead Acne
Prevention is always better than cure! Here’s how to keep your forehead clear:
- Avoid Tight Hats or Headbands: They trap sweat and oil, which can clog pores.
- Steer Clear of Hair Gels: These can transfer to your skin and cause breakouts.
- Wash Your Hair Daily: Oily, unwashed hair in contact with your skin can worsen acne.
- Use Gentle Cleansers: Wash your face twice daily with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser.
- Remove Makeup Before Bed: Letting makeup sit overnight clogs pores and invites breakouts.
- Don’t Touch Your Face: Your hands carry bacteria—keep them off your skin!
- Wash Your Face After Sweating: Sweat can trap bacteria and dirt in your pores.
- Use a Clarifying Face Mask: A couple of times a week, opt for a mask to tighten pores and reduce inflammation.
FAQs About Forehead Acne
Q1: What causes forehead pimples?
Excess oil, dead skin cells, dirt, bacteria, and fungi clogging pores are the main culprits.
Q2: Can my hair products cause acne?
Yes! Hair products with oils, sulfates, or coconut oil can transfer to your forehead and clog pores.
Q3: Does stress play a role in acne?
Stress increases cortisol, which can lead to oil overproduction and breakouts.
Q4: Can diet trigger forehead acne?
High-sugar, high-glycemic foods can worsen inflammation and acne. Opt for anti-inflammatory foods instead.
Q5: What’s the best way to treat forehead acne?
A combination of benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinol is highly effective for treating most types of forehead acne.
Final Thoughts
Forehead acne might be a pain, but it’s far from unbeatable. With the right routine, products, and a few tweaks to your lifestyle, you can achieve the clear, glowing skin you deserve.
Consistency is key—stick to a routine and give your skin time to heal. If breakouts persist, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice. Your skin’s glow-up is just around the corner!
Shop:
Best acne treatment cream for acne on the forehead
Best acne treatment cleanser for acne on the forehead
References
- Sebum analysis of individuals with and without acne
- Are your hair care products causing breakouts?
- Comedogenicity of current therapeutic products, cosmetics, and ingredients in the rabbit ear
- The response of skin disease to stress: changes in the severity of acne vulgaris as affected by examination stress
- Topical retinoids for acne
- Topical retinoids in acne--an evidence-based overview
To find the right acne treatments for your unique skin, take the free skin assessment by clicking here.



